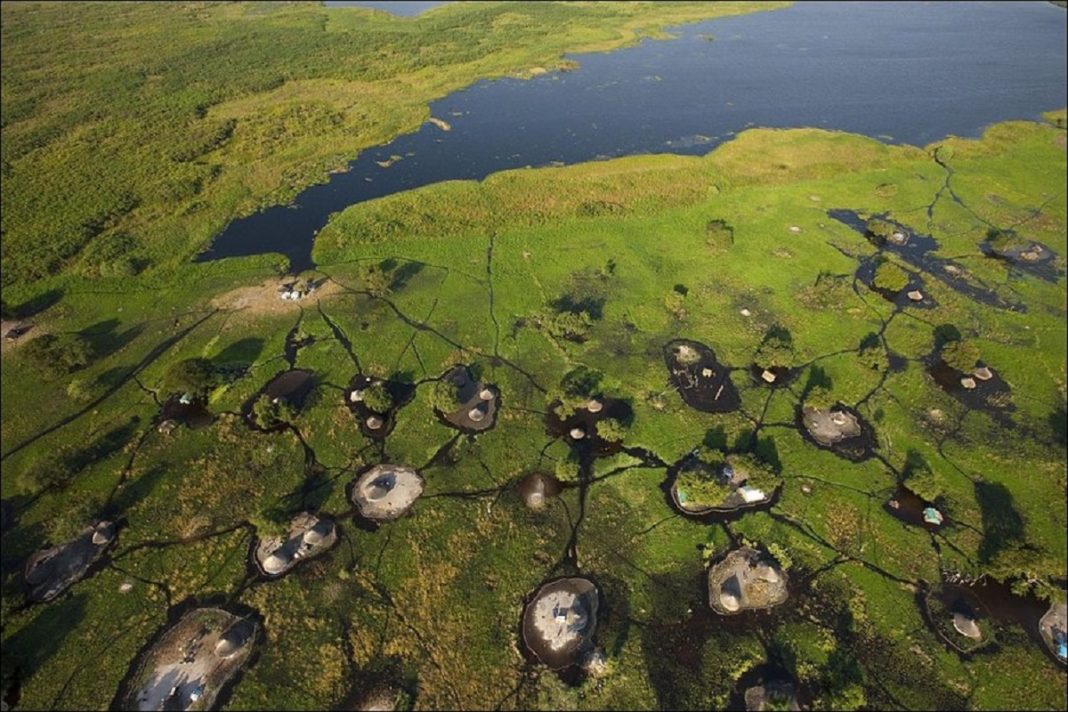
The Sudd is a vast swamp in South Sudan, formed by the White Nile’s Baḥr al-Jabal section. The Arabic word sudd is derived from sadd, meaning “barrier” or “obstruction”. The term “the sudd” has come to refer to any large solid floating vegetation island or mat. The area that the swamp covers is one of the world’s largest wetlands and the largest freshwater wetland in the Nile Basin.
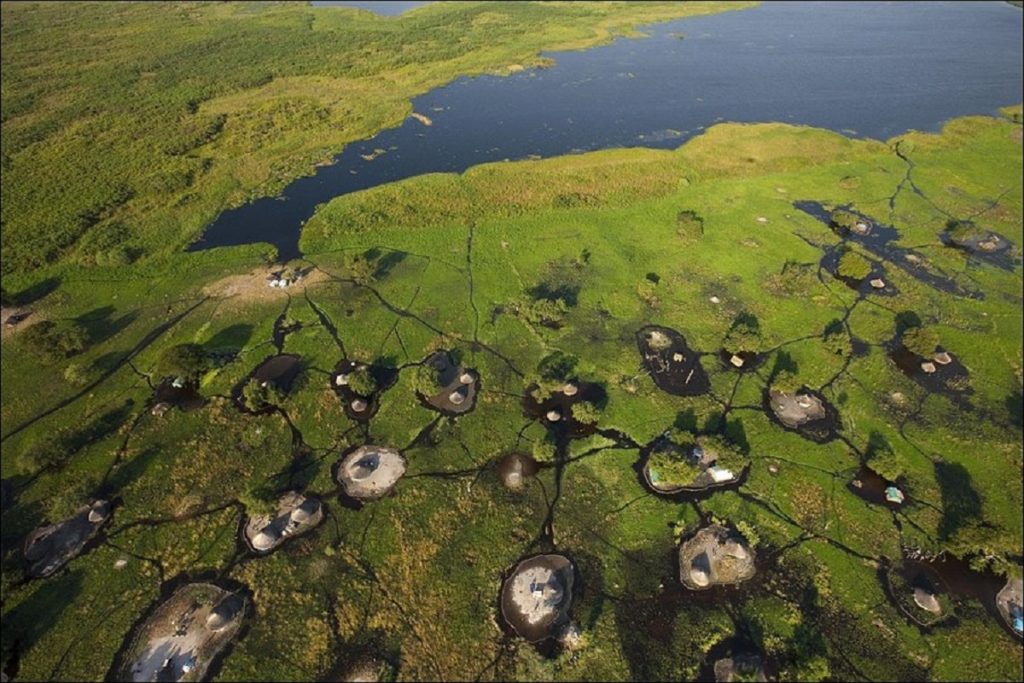

The Sudd stretches from Mongalla to just outside the Sobat River confluence with the White Nile just upstream of Malakal as well as westwards along the Bahr el Ghazal. The shallow and flat inland delta lies between 5.5 and 9.5 degrees latitude North and covers an area of 500 kilometers south to north and 200 kilometers east to west between Mongalla in the south and Malakal in the north.

Its size is highly variable, averaging over 30,000 square kilometers. During the wet season, it may extend to over 130,000 square kilometers comprising 21% of the country, depending on the inflowing waters, with the discharge from Lake Victoria being the main control factor of flood levels and area inundation. Since the Sudd area consists of various meandering channels, lagoons, reed, and papyrus fields and loses half of its inflowing water through evapotranspiration in the permanent and seasonal floodplains, the complex hydrology has many primary and secondary effects.3

Nuer and Dinka pastoralists use the Sudd and the surrounding areas extensively. Livestock and rain-fed agriculture are the dominant means of support for the largely rural population for which the seasonally flooded grasslands along the Sudd provides valuable grazing lands.
The vegetation cover of the area can generally be classified into five categories which depend on the elevation of the area above river flood level: the lakes and rivers, the floating plant life of the swamp, river-flooded grasslands (Toic), rain-flooded grasslands, and wooded grasslands on the fringes. Grassland and woodland areas have been cultivated by local populations.
The long-running civil war in Southern Sudan seriously disrupted conservation efforts in the Sudd, especially as the widespread availability of weapons has encouraged wildlife poaching, including elephants.
According to Wikipedia/ sudantribune/ atlasobscura