A plasma torch is a device that generates a constant flow of plasma – the fourth state of matter. In this state, matter is superheated, and electrons are ripped away from the matter, resulting in an ionized gas. This gas can be used to cut electrically conductive materials precisely and, therefore, find use in industrial applications. Inert gases such as helium, neon, and argon are typically used in plasma torches. Argon mixed with hydrogen is the industry’s most common gas mixture since it is cost-effective and produces the hottest flame and clearest cuts.
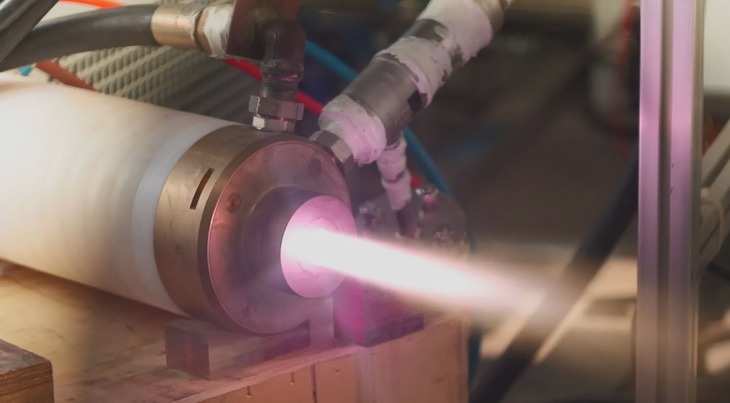

In all these applications, the cathode gets depleted and needs to be replenished. This limits the lifespan of the torch while increasing the maintenance costs associated with the equipment.
A research team led by Zhao Peng, a professor at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, has found a simple and effective solution to the cathode depletion problem. The work done under the aegis of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a continuous feed system for the cathode that can rapidly replenish old, worn-out ones without interrupting the plasma torch.
Conventional plasma torches typically run for 160 hours. However, with the cathode being continuously fed, this is the least the new plasma torch can do. With their innovation, the team has allowed plasma torches to run for long periods, thereby reducing their downtime and maintenance costs.
This will further improve the efficiency of the process and lead to the development of more industrialized applications of the plasma torch.
According to the interestingengineering