Nikola Tesla was an engineer and scientist known for designing the alternating-current (AC) electric system, which is the predominant electrical system used across the world today. He also created the “Tesla coil,” which is still used in radio technology.
Born in modern-day Croatia, Tesla came to the United States in 1884 and briefly worked with Thomas Edison before the two parted ways. He sold several patent rights, including those to his AC machinery, to George Westinghouse.
Early Life

Tesla was born in Smiljan, Croatia, on July 10, 1856.
Tesla was one of five children, including siblings Dane, Angelina, Milka and Marica. Tesla’s interest in electrical invention was spurred by his mother, Djuka Mandic, who invented small household appliances in her spare time while her son was growing up.
Tesla’s father, Milutin Tesla, was a Serbian orthodox priest and a writer, and he pushed for his son to join the priesthood. But Nikola’s interests lay squarely in the sciences.
Education
After studying at the Realschule, Karlstadt (later renamed the Johann-Rudolph-Glauber Realschule Karlstadt) in Germany; the Polytechnic Institute in Graz, Austria; and the University of Prague during the 1870s, Tesla moved to Budapest, where for a time he worked at the Central Telephone Exchange.
It was while in Budapest that the idea for the induction motor first came to Tesla, but after several years of trying to gain interest in his invention, at age 28 Tesla decided to leave Europe for America.
First Solo Venture

In 1885, Tesla received funding for the Tesla Electric Light Company and was tasked by his investors to develop improved arc lighting. After successfully doing so, however, Tesla was forced out of the venture and for a time had to work as a manual laborer in order to survive.
His luck would change two years later when he received funding for his new Tesla Electric Company.
Inventions

Throughout his career, Tesla discovered, designed and developed ideas for a number of important inventions — most of which were officially patented by other inventors — including dynamos (electrical generators similar to batteries) and the induction motor.
He was also a pioneer in the discovery of radar technology, X-ray technology, remote control and the rotating magnetic field — the basis of most AC machinery. Tesla is most well-known for his contributions in AC electricity and for the Tesla coil.
AC Electrical System
Tesla designed the alternating-current (AC) electrical system, which would quickly become the preeminent power system of the 20th century and has remained the worldwide standard ever since. In 1887, Tesla found funding for his new Tesla Electric Company, and by the end of the year, he had successfully filed several patents for AC-based inventions.
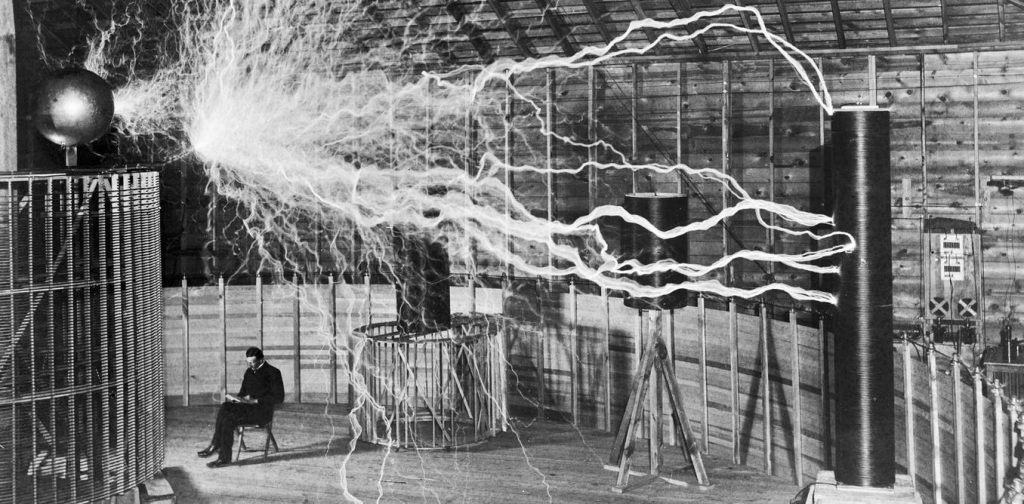

Tesla’s AC system soon caught the attention of American engineer and businessman George Westinghouse, who was seeking a solution to supplying the nation with long-distance power. Convinced that Tesla’s inventions would help him achieve this, in 1888 he purchased his patents for $60,000 in cash and stock in the Westinghouse Corporation.
As interest in an AC system grew, Tesla and Westinghouse were put in direct competition with Thomas Edison, who was intent on selling his direct-current (DC) system to the nation. A negative press campaign was soon waged by Edison, in an attempt to undermine interest in AC power.