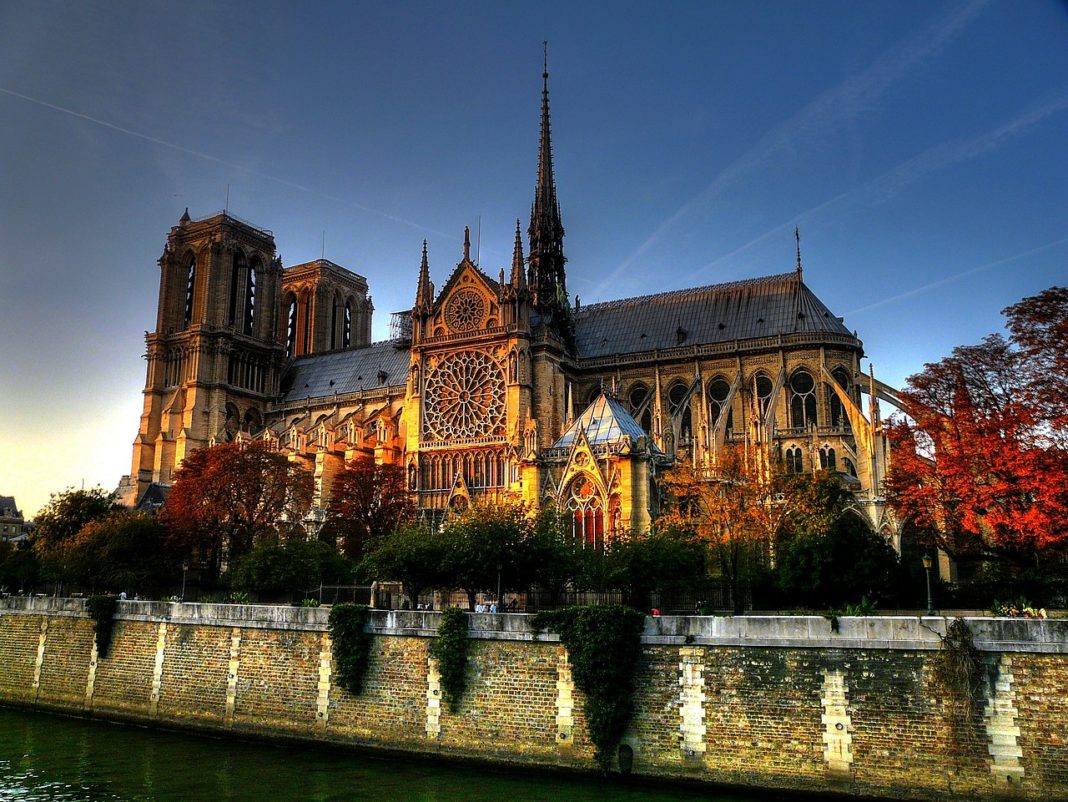
The cathedral, dedicated to the Virgin Mary, is considered one of the finest examples of French Gothic architecture. Several of its attributes set it apart from the earlier Romanesque style, particularly its pioneering use of the rib vault and flying buttress, its enormous and colorful rose windows, and the naturalism and abundance of its sculptural decoration. Notre Dame also stands out for its musical components, notably its three pipe organs (one of which is historic) and its immense church bells.
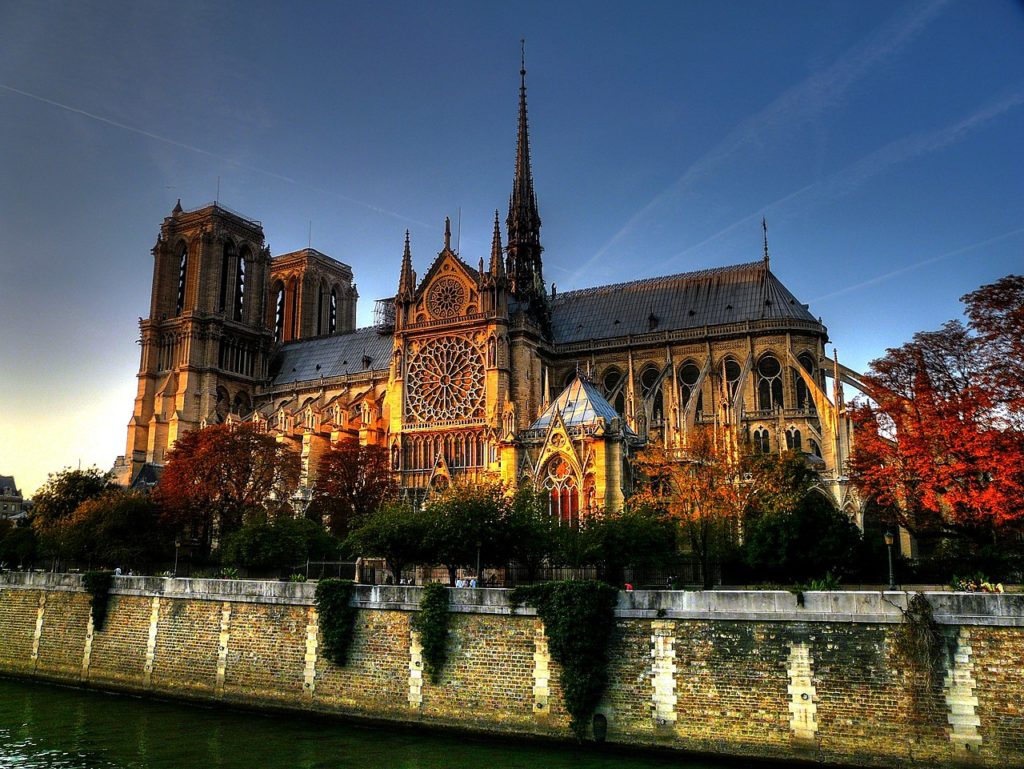

Construction of the cathedral began in 1163 under Bishop Maurice de Sully and was largely completed by 1260, though it was modified frequently in the centuries that followed.
The 1831 publication of Victor Hugo’s novel Notre-Dame de Paris (known in English as The Hunchback of Notre-Dame) inspired popular interest in the cathedral, which led to a major restoration project between 1844 and 1864, supervised by Eugène Viollet-le-Duc. On August 26, 1944, the Liberation of Paris from German occupation was celebrated in Notre-Dame with the singing of the Magnificat. Beginning in 1963, the cathedral’s façade was cleaned of centuries of soot and grime. Another cleaning and restoration project was carried out between 1991 and 2000.

The cathedral is one of the most widely recognized symbols of the city of Paris and the French nation. In 1805, it was awarded the honorary status of a minor basilica. As the cathedral of the archdiocese of Paris, Notre-Dame contains the cathedral of the archbishop of Paris (Laurent Ulrich).
In the early 21st century, approximately 12 million people visited Notre-Dame annually, making it the most visited monument in Paris. The cathedral has long been renowned for its Lent sermons, a tradition founded in the 1830s by the Dominican Jean-Baptiste Henri Lacordaire. In recent years, these sermons have increasingly often been given by leading public figures or government-employed academics.

Over time, the cathedral has gradually been stripped of many of its original decorations and artworks. However, the cathedral still contains several noteworthy examples of Gothic, Baroque, and 19th-century sculptures, a number of 17th- and early 18th-century altarpieces, and some of the most important relics in Christendom – including the Crown of Thorns, a sliver of the true cross and a nail from the true cross.

On 15 April 2019, just before 18:20 CEST, a fire broke out beneath the roof of the Notre-Dame cathedral in Paris. By the time the structure fire was extinguished, the building’s spire had collapsed, most of its roof had been destroyed, and its upper walls were severely damaged. Extensive damage to the interior was prevented by its stone vaulted ceiling, which largely contained the burning roof as it collapsed. Many works of art and religious relics were moved to safety early in the emergency, but others suffered smoke damage, and some of the exterior art was damaged or destroyed. The cathedral’s altar, two pipe organs, and three 13th-century rose windows suffered little or no damage. French President Emmanuel Macron said that the cathedral would be restored by 2024.
According to Wikipedia