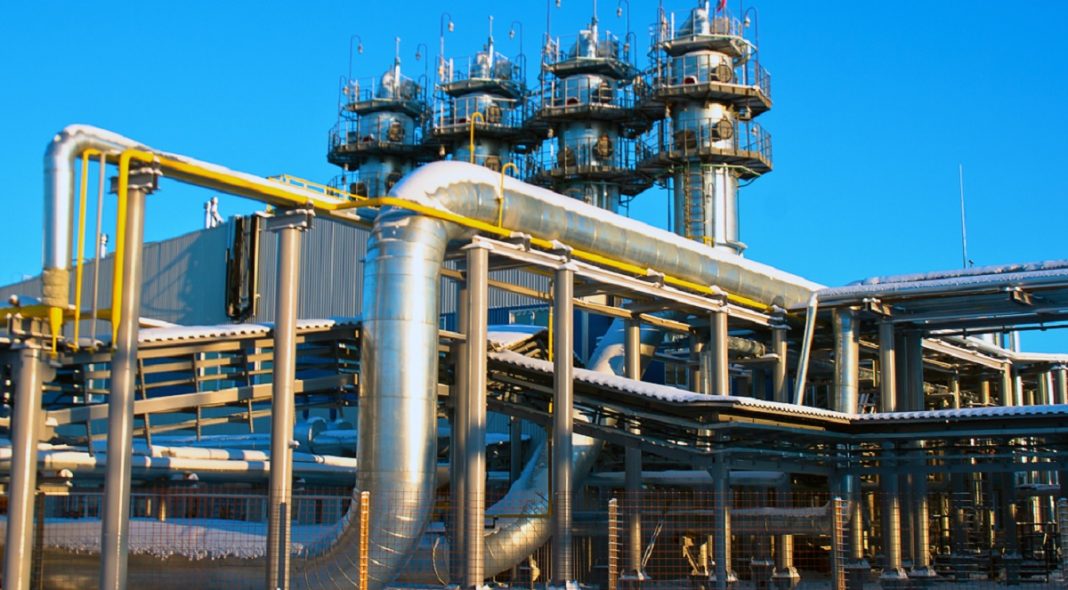
The West-East Gas Pipeline is operated by PetroChina, which has a 72.26% interest in PetroChina Pipelines. Upon full completion, it will top the list of the world’s longest pipelines. It comprises a main trunkline (phase I) and eight branches. Phase I connects the Tarim Basin gas fields in Xianjing to China’s biggest city, Shanghai, stretching 4,000km. The pipeline passes through no fewer than 66 cities in ten provinces, and the gas is used for electricity production in the Yangtze River Delta.
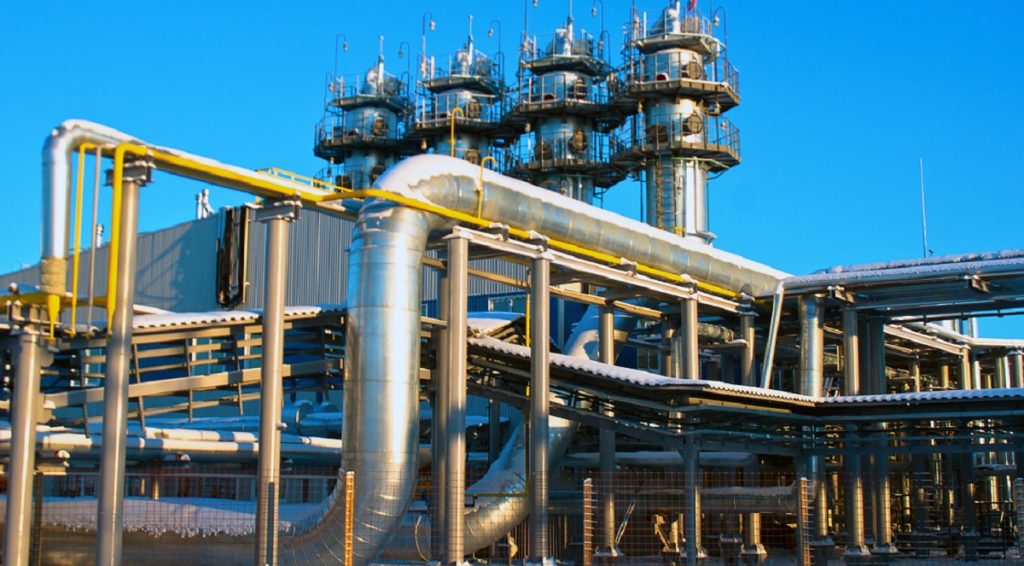

The construction of the West-East Gas Pipeline started in 2002. The pipeline was put into trial operation on 1 October 2004, and the full commercial supply of natural gas commenced on 1 January 2005. The pipeline is owned and operated by PetroChina West-East Gas Pipeline Company, a subsidiary of PetroChina.
Originally having the capacity to hold 12 billion cubic meters of natural gas per year, the pipeline was expanded to 17 billion cubic meters in 2007. Ten new gas compressor stations were built to support the extra gas. The pipeline is supplied from the Tarim Basin oil and gas fields in Xinjiang province. The Changqing gas area in Shaanxi province is a secondary gas source. In the future, the planned Kazakhstan-China gas pipeline will be connected to the West-East Gas Pipeline.
Currently, the first three-phase were completed. The fourth pipeline will start from the Tarim Basin or from Sichuan. The total length of the third pipeline is 7,378 kilometers, including a 5,220-kilometer trunkline and eight branches. In addition, the project includes three gas storage and an LNG plant. It will have a capacity of 30 billion cubic meters of natural gas per year with an operating pressure of 10–12 megapascals (1,500–1,700 psi). The pipeline will be supplied from Central Asia–China gas pipeline’s Line C supplemented by supplies from the Tarim basin and coalbed methane in Xinjiang.
According to wikipedia