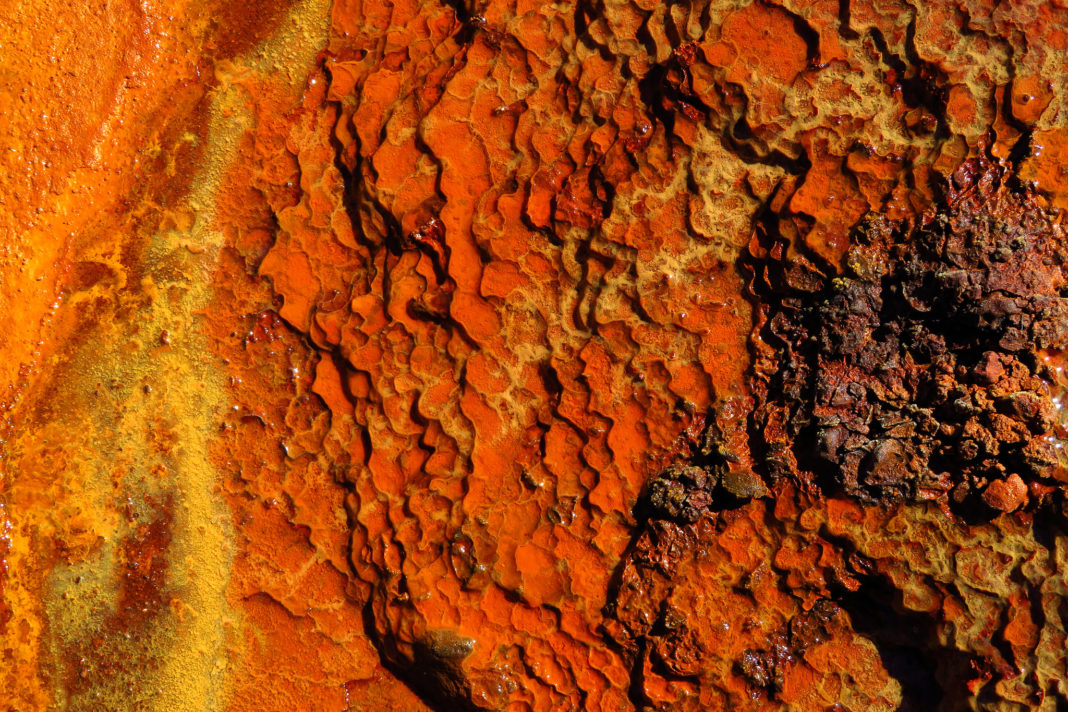
Wilgie Mia, also called Thuwarri Thaa (‘red ochre hole’) is an ochre mine in the Weld Range of Western Australia. It has been in use for 27,000-40,000 years, during which an estimated 14,000 cubic meters of ochre and rock was mined. This has led to suggestions that Wilgie Mia is the world’s oldest continuing mining operation.
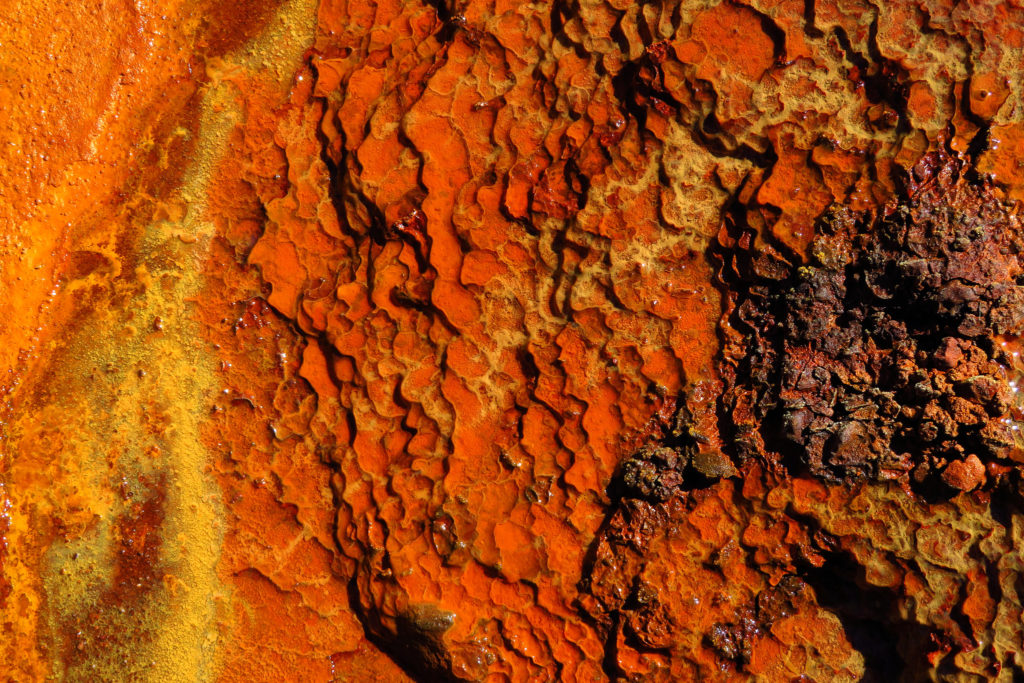

Wilgie Mia is the largest and deepest historic Aboriginal ochre mine in Australia. Worked to a depth of 20 meters, scaffolds had lined the seam face beyond an opening 30 meters across. Archaeological excavations have recovered tools and equipment used in the exploitation of the resource.

Wilgie Mia and its surrounding area are of major and ongoing cultural significance and sacredness to the Wajarri Yamatji people and their neighbors. The local creation story tells that the red ochre at Wilgie Mia was formed by the blood of a red kangaroo that died there.

Ochre has been an important commodity in the history of Australia, and Wilgie Mia produced large amounts of both red and yellow pigments. A range of colors and high durability are found in the constituent clays of the ochre mined at Wilgie Mia. These are residual to a geological process involving haematite (Fe2O3) and other iron-rich compounds.
Scientific analysis of ochre reveals the extensive use of Wilgie Mia ochre throughout Western Australia. Wilgie Mia ochre has been used in the production of rock art and other painting practices throughout many regions of Australia.
The mine continues to export ochre as a commercial pigment. Aboriginal miners also continue to extract ochre for use in ceremonies, art, and healing practices. Wilgie Mia was added to the Australian National Heritage List in 2011. In 2018 the Wajarri Yamatji people obtained exclusive possession native title of the site.
According to Wikipedia