Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. is a British-American company known for publishing the Encyclopædia Britannica, the world’s oldest continuously published encyclopaedia, as well as extensive digital efforts—including text and audiovisual—that are aimed at educational tools for primary and secondary schools, and for everyday learners accessing information through online search.

The company was founded in Edinburgh, Scotland, in the 18th century, during the historical period termed the Scottish Enlightenment. Colin Macfarquhar and Andrew Bell began the first edition in 1768.
In 2009, Britannica Global Edition was printed with 30 volumes. It contained over 40,000 articles and 8,500 photographs.

In 2012, after 244 years, Britannica ended the print editions, with the 32 volumes of the 2010 encyclopædia being the last to be printed in the traditional hard-bound volumes. By the time the company had stopped publishing the print editions, printed sales only represented about 1% of their business. Since then, Britannica has published the encyclopedia exclusively online.
In 2018, the company released Britannica Insights, an extension for the Chrome web browser. The extension supplements Google’s featured snippets with accurate information. In 2019, in a partnership with Binumi, Britannica released a video product that gives schools the opportunity to use millions of royalty-free multimedia clips to create digital storytelling projects about content they are already teaching.
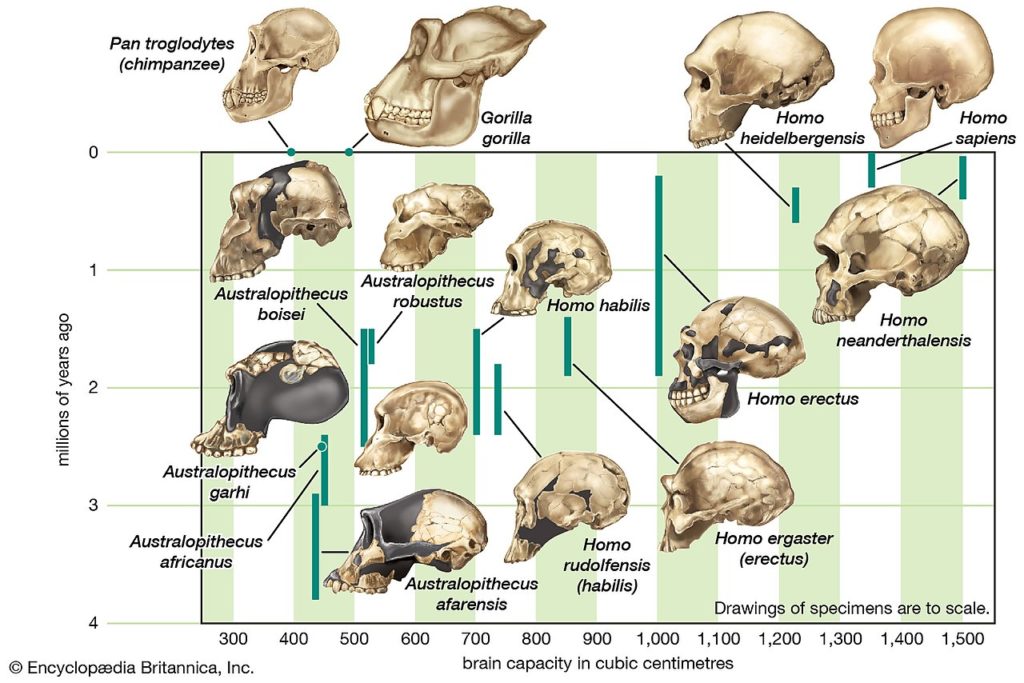
In 2020, Encyclopædia Britannica released the Britannica All New Children’s Encyclopedia: What We Know and What We Don’t, an encyclopedia aimed primarily at younger readers, covering major topics. The encyclopedia was widely praised for bringing back the print format. It was Britannica’s first encyclopedia for children since 1984.
According to Wikipedia