Omron Corporation is a Japanese electronics company based in Kyoto, Japan. Omron was established by Kazuma Tateishi in 1933.
Omron’s primary business is the manufacture and sale of automation components, equipment, and systems. In the consumer and medical markets, it is known for medical equipment such as digital thermometers, blood pressure monitors, and nebulizers.

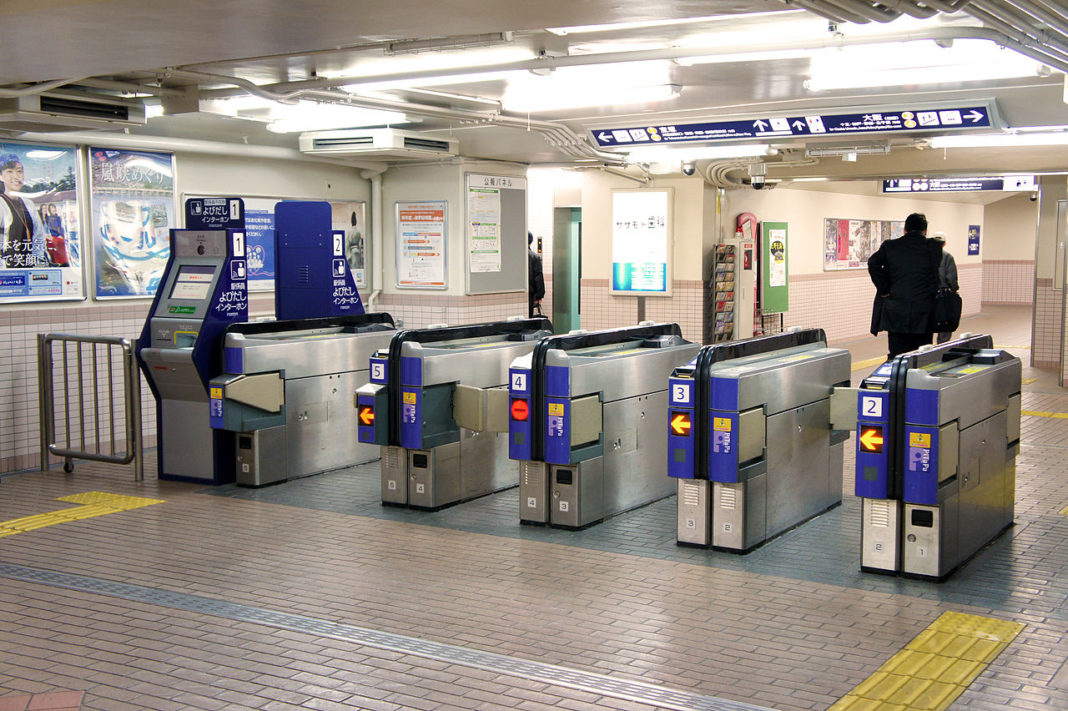
Omron developed the world’s first electronic ticket gate, which was named an IEEE Milestone in 2007, and was one of the first manufacturers of automated teller machines (ATM) with magnetic stripe card readers. The system consisted of machines that accepted punch-card commuter passes and machines that handled regular tickets with magnetically recorded (barcode) information.

Later, the Congress of Japan Railway Cybernetics (CJRC) established magnetic recording as the standard data recording technology for ticket gate machines. In response, Kintetsu and OMRON jointly developed an automated gate machine that met the CJRC’s standards with its ability to read magnetic commuter pass cards in 1971. In April of the same year, automated ticket gate machines were installed and put into operation at Kintetsu Railway’s 19 stations including Osaka-Abenobashi station. This large-scale, simultaneous deployment prompted many other railway companies to introduce automated ticket gates in their own systems.
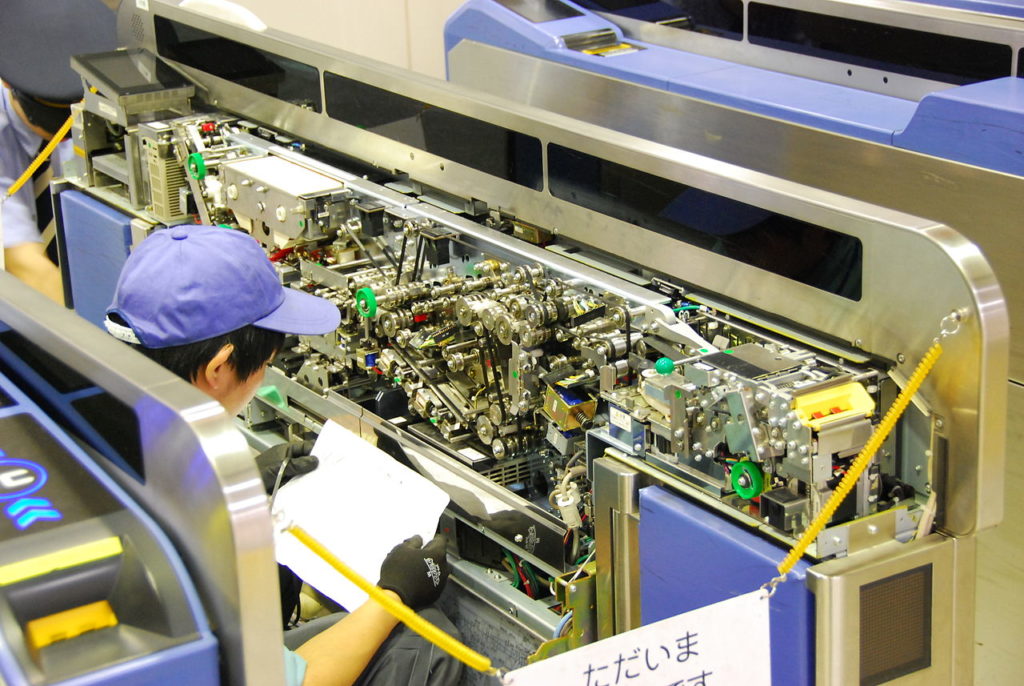

Recently, the deployment of automated ticket gates compatible with contactless IC cards has spread throughout Japan. At the same time, more and more rail, subway, bus, and other service companies allow the common use of a single IC card. New applications of automated ticket gates that go beyond inspecting train pass/tickets are also being promoted, such as OMRON’s new ‘Anshin Goopas’ (Goopas Child Safeguard). This service is designed to send an email notification to a parent’s mobile phone when a child commuting to school passes through a ticket gate using a specific IC card.
According to the Wikipedia